Understanding the complexities of the human body has always been at the core of medical science. Over the years, traditional learning methods such as textbooks and cadaver dissections have paved the way for more advanced and interactive tools. One such advancement is the 3D anatomy model, which offers an immersive and detailed perspective of human anatomy. By enabling users to explore organs, bones, muscles, and other structures in a three-dimensional format, this technology is transforming how students, educators, and professionals engage with the human body.
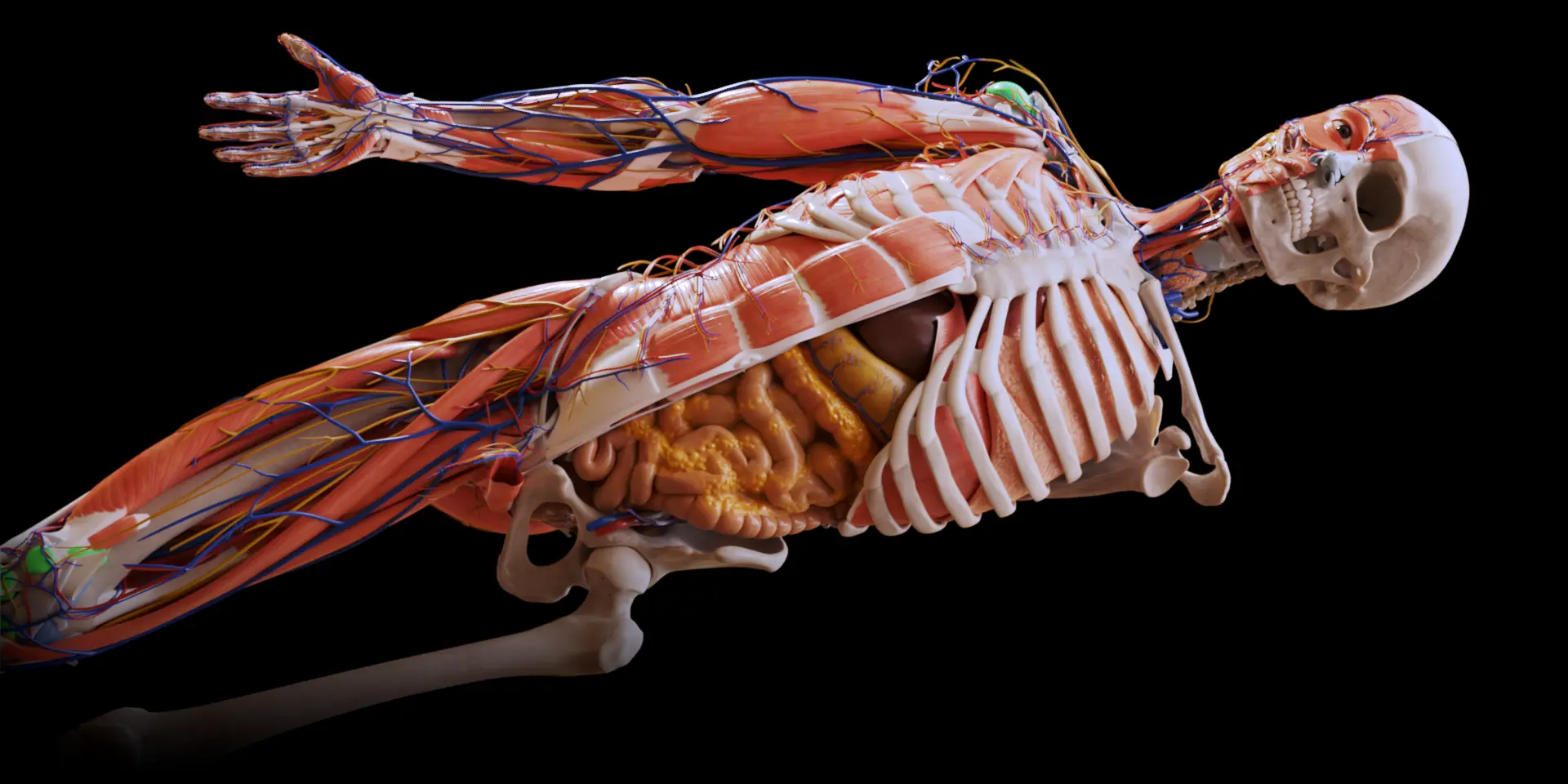
The 3D anatomy model allows learners to visualize the spatial relationships between anatomical structures in a way that two-dimensional diagrams simply cannot. Instead of flipping through pages or examining static images, users can rotate, zoom, and dissect layers of the model to gain a more intuitive understanding of form and function. This interactive experience is particularly beneficial in fields like medicine, physical therapy, and biology, where precise knowledge of anatomy is crucial. As such, the 3D anatomy model has become an indispensable resource in modern education.
In addition to its educational applications, the 3D anatomy model is proving invaluable in clinical settings. Surgeons and medical professionals use these models to plan complex procedures, simulate surgeries, and explain diagnoses to patients. A 3D anatomy model can be customized to reflect a patient’s unique physiology based on medical imaging data, making it a powerful tool for personalized medicine. This level of detail not only enhances procedural accuracy but also improves communication between doctors and their patients.
One of the significant advantages of using a 3D anatomy model is the accessibility it offers. With the rise of digital learning platforms, these models are now available on tablets, laptops, and VR headsets, making them more convenient and engaging than ever before. Medical schools and institutions around the world are adopting this technology to bridge gaps in traditional learning and to offer a more dynamic educational experience. Whether in a classroom or at home, students can explore the human body in real-time using a 3D anatomy model tailored to their curriculum.
Furthermore, the use of a 3D anatomy model supports a more inclusive and sustainable approach to anatomical education. Cadaver dissection, while valuable, presents ethical, logistical, and environmental challenges. The digital alternative reduces the need for physical specimens and provides a repeatable learning experience without degradation over time. By replacing or supplementing traditional methods, the 3D anatomy model contributes to a more ethical and efficient way of teaching human biology.
The benefits of the 3D anatomy model are not limited to medical and educational fields. Artists, fitness professionals, and sports coaches also utilize these models to better understand human motion and structure. For example, an animator can study a 3D anatomy model to create lifelike character movements, while a personal trainer may use it to demonstrate muscle function during exercise. This versatility highlights the wide-reaching impact of the technology across diverse disciplines.
As technology continues to evolve, the 3D anatomy model is becoming increasingly sophisticated. Modern versions often include augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) integrations, adding another layer of interactivity. These innovations allow users to step inside the human body and explore it as if they were part of it. The immersive nature of such experiences enhances memory retention and comprehension, making the 3D anatomy model a cutting-edge tool in both learning and professional development.
There are also numerous software platforms available that provide access to high-quality 3D anatomy models, many of which include quizzes, annotations, and multi-language support. These features allow educators to customize lessons and track student progress more effectively. The ability to interact with a 3D anatomy model through a digital platform ensures that learning is both engaging and adaptable to different learning styles, particularly for visual and kinesthetic learners.
Despite its many advantages, it is important to recognize the limitations of the 3D anatomy model. While it excels in visualization and accessibility, it cannot fully replace hands-on experience with real tissues and organs. For this reason, it is most effective when used in conjunction with traditional methods rather than as a standalone solution. Nonetheless, the 3D anatomy model continues to play a critical role in enhancing anatomical education and preparing the next generation of healthcare professionals.
In conclusion, the 3D anatomy model represents a monumental leap forward in how we learn about and interact with the human body. From improving medical education and surgical planning to aiding artists and fitness experts, this innovative tool offers endless possibilities. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of the 3D anatomy model will only expand, further solidifying its place as a cornerstone of modern anatomy education and practice.
